EE2.sad: Exercises
[ Home | Syllabus | Exercises | Coursework | Exams ]
[
Wk 2 |
Wk 4 |
Wk 6 |
Wk 8 |
Wk 10 |
Wk 12
]
Week 2
The farmer, fox, goose and grain:
A farmer wants to move himself, a silver fox, a fat goose and some tasty wheat grain across a river. His boat is very small and he can only take one of these things at at time with him. An unattended fox will eat the goose and, if he's not there to watch the goose, it will eat the grain. So, he must not leave the fox alone with the goose, or the goose alone with the grain. What is he to do?
Your challenge comes in three parts:
- to solve the riddle yourself;
- to consider five representations of the solution [ 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, ] (campus only);
- to choose two of them and to write a paragraph on how these solutions break the problem down and how clearly they show the blueprint for the farmer to get the fox, the goose and grain to the other side of the river.
Week 4
Pseudo code:- Using pseudo code, write out the commands a computer would
need to perform to compute the following equation:
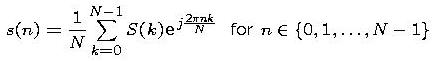
- What is the function of the following algorithm, described using pseudo code?
val = A[1]
for i = 2 to length[A]- if val > A[i]
- then val = A[i]
- endif
endfor
return val - if val > A[i]
- Look at these two examples and draw up a set of guidelines for writing pseudo code: example 1, example 2 (©IEEE 2003)?
-
From the scenario description
for part of the Medical Health Practice system,
produce the corresponding DFD fragment (at level 0).
- Using the scenario description from CD Selections' internet sales system, produce the DFD fragment at level 0.
- Using the same scenario description, produce the entire DFD for this process down at level 1.
- Do you notice any inconsistencies between your diagrams?
- What is the term given to adjusting DFDs to make the different levels consistent again?
Week 6
Analysis:- Which of the following are kinds of viewpoint for a design?
- structural
- behavioural
- compositional
- functional
- incremental
- experimental
- data-modelling
- wicked
- process-modelling
- technical
- Which viewpoint is given by a state-transition diagram?
- Which viewpoint is given by an entity-relationship diagram?
- Which viewpoint is given by pseudo-code?
- How many data flows are there in the CD Selections logical DFD?
- In an ERD, an identifier is a type of what?
- Sketch the Structure Chart for the HTML file (to see contents [View | Page Source], or open file in a text editor). Hint: you should use about ten or a dozen boxes.
- From this JSD, give an example of (i) a selection item, (ii) a sequence item, (iii) an iteration item.
Week 8
Jackson structure diagrams:- A report is to be produced. Each page contains 42 detail lines in addition to page headings and a total line. The total line includes appropriate text, indicating that it may be a grand total or a cumulative carried forward. Produce a sketch of a sample report, annotate it, then draw the logical data structure for the report file. [solution 3.3.1]
- Produce an annotated sketch and then the logical data structure for a file of self-adhesive labels where the labels are "3-up" across the page. The labels may contain 3 or 4 lines of print. You may assume that a row of labels can be constructed in memory and that a complete row can be printed before moving onto the next one. This means that you can consider a row as a component containing a number of labels (in this case 3), each of which may contain 3 or 4 lines. [solution 3.3.2]
- A file contains three different types of records (type 1, type 2, type 3). Records of type 1 are processed by summing the amounts. Records of type 2 are processed according to a region code - if the code is A the record is displayed, otherwise the first 20 characters only are displayed. Records of type 3 are ignored. First produce an annotated sketch for some sample data, then draw the logical data structure of the file in respect of the above problem. (Remember that the structure diagram should reflect the way that the data are to be processed, but it does not contain any processing details, such as "accumulate the amounts" or "display record".) [solution 3.3.3]
- A production file contains a number of records about machines, indicating whether or not they are due for replacement. It is required to produce a duplicate file with one extra record at the end containing a count of the machine that are due for replacement Produce a suitable program structure diagram. [solution 4.3.1]
- A hospital file contains records of staff and patients sorted into ascending order of surname within ward. Design the structure of a program to print all the names of the staff in ward order, with a heading at the start of each ward. [solution 4.3.2]
Week 10
Coupling and Cohesion:- For each of the following examples, determine what kind of
coupling is exhibited:
- Now, go through the examples again, but this time determine which kind of cohesion each one shows.
Week 12
Testing:- Explain the difference between alpha and beta testing.
- Explain the difference between black box and white box testing.
- Draw the logic-flow diagram for the bubble sort program bubble.c
- The requirements specification for a procedure that interrogates
an exam database states the following:
The database interrogation procedure searches the exam database for all entries that match the fields passed into the procedure. The procedure returns a pointer to a linked list of the matching records or a NULL pointer in the event that there is not a match. The procedure takes, as input, a value for each of the fields in the database record. A field with a blank entry or zero value should be interpreted as a "don't care" value. Each database record has the following fields for each candidate:
Construct a minimum set of black box tests for this procedure.
wherecand_name: char(20) first 20 characters of the student's full name cand_URN: digit(7) university registration number, which starts with a '1' cand_year: int8(1) student's year group (in the range 1-5) cand_mod1: grade(1) grade for first module cand_mod2: grade(1) grade for second module cand_mod3: grade(1) grade for third module cand_mod4: grade(1) grade for fourth module cand_mod5: grade(1) grade for fifth module cand_ovrl: grade(1) overall grade
digit denotes a character between '0' and '9';
int8 is an eight-bit (1-Byte) integer;
grade denotes a character between 'A' and 'F' or 'S',
i.e., from the set {A, B, C, D, E, F, S}.
- From the logic-flow diagram, construct a minimum set of white box tests and hence a test oracle for the procedure.